Vaccination
Classification of Live Vaccines
Live vaccines are classified into three groups according to their ability to break through ever increasing levels of MDA.
- Mild – these vaccine strains are highly attenuated, breaking through very low levels of MDA and are thus no longer applicable in the commercial environment.
- Intermediate – attenuated IBDV strains breaking through MDA titres ≤ 6 log2 VN (VN of Merck Animal Health) (ELISA (IDEXX standard) titre 125).
- Intermediate Plus/Hot – attenuated IBDV strains breaking through MDA titres ≤ 8 log2 VN (VN of Merck Animal Health) (ELISA (IDEXX standard) titre 500).
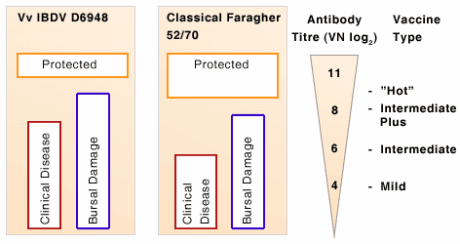
Schematic representation of IBDV titres (VN log2) required to protect against IBD infection with a very virulent (D6948) and a classical (Faragher 52/70) IBDV strain. Maximum breakthrough titres of the different vaccine types are represented on the right.
A potential disadvantage of live IBDV vaccines is inherent pathogenicity. This is specifically applicable to intermediate plus type vaccines and even more so in the case of so called “hot” vaccines. These vaccines must never be administered to chickens in the first 10 days post hatch. Bursal damage caused may result in immunosuppression.
New developments in the field of IBDV vaccines include:
- Virus-Antibody Complex Vaccines:
Antibody (immunoglobulin) specific for the virus used in the vaccine is mixed in an appropriate ratio with the vaccine virus. This process results in a virus-antibody complex (immune complex) vaccine. The amount of antibody in the complex is so small that it does not provide passive immunity or neutralise the vaccine virus. On the other hand, the amount of antibody added to the vaccine is enough to delay by several days the normal course of vaccine virus replication.This allows for the safe - HVT Recombinant Vaccine:
The concept of recombinant vaccines is to insert genes of critical immunising epitopes of a disease agent (IBDV) into nonessential geneloci of a vector virus (HVT – herpesvirus of turkeys). Vaccination with the recombinant virus thus results in immunization against both the vector virus as well as the expressed epitopes of the disease agent.
Peer Reviewed by Dr J J (Sjaak) de Wit and William Baxendale.

